Gaming PCs have evolved into powerhouses capable of delivering breathtaking graphics and seamless performance. However, with great power comes great heat, and managing this heat is critical to maintaining optimal performance and longevity. PC cooling systems are the unsung heroes of gaming PCs, ensuring that components like CPUs and GPUs stay within safe temperature ranges.
In this article, we’ll dive into the mechanics of gaming PC cooling systems, exploring how they work, the different types available, and the innovative technologies that keep your rig running cool under pressure.
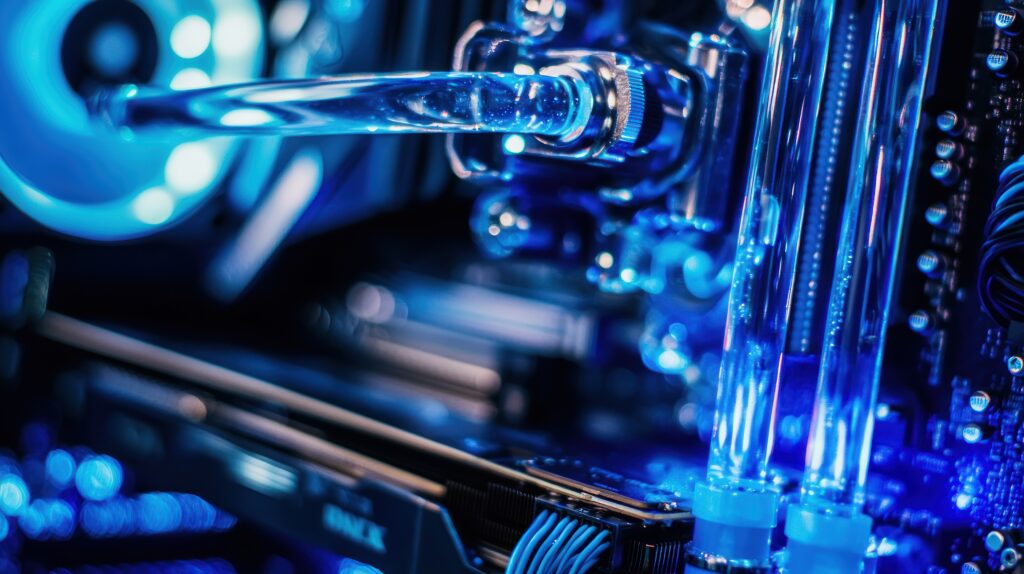

The basics of PC cooling
At its core, a gaming PC cooling system dissipates heat generated by the computer’s components. When your CPU or GPU processes data, it converts electrical energy into heat. If this heat isn’t managed effectively, it can lead to thermal throttling, reduced performance, or even permanent damage to the hardware. Cooling systems or liquid coolers work by transferring heat away from these components and expelling it into the surrounding environment.
The two primary types of cooling systems include air cooling and liquid cooling. Air cooling relies on heatsinks and fans to draw heat away from components, while liquid cooling uses a coolant to absorb and transport heat to a radiator, where it is then dissipated.
Innovative cooling technologies
PC cooling technology has also advanced to meet the demand. One such innovation is the use of diaphragm pumps in custom liquid cooling loops. Diaphragm pumps are known for their reliability and precision. These pumps use a flexible diaphragm to move coolant through the system, providing consistent flow rates and reducing the risk of leaks. Learn more about knf.com/en/uk.
Another cutting-edge technology is phase-change cooling, which operates on the same principles as a refrigerator. In this system, a refrigerant is used to absorb heat from the CPU or GPU, causing it to evaporate. The vapour is then compressed and cooled, turning it back into a liquid to complete the cycle. While phase-change cooling is highly effective, it is also complex and expensive, making it more suitable for extreme overclocking rather than everyday use.

Air cooling: Simplicity and efficiency
Air cooling is the most common and cost-effective method for cooling gaming PCs. It consists of a heatsink, which is a block of metal (usually aluminium or copper) with fins to increase its surface area, and a fan that blows air over the heatsink to carry heat away. The heatsink is attached directly to the CPU or GPU using thermal paste, which ensures efficient heat transfer.
One of the key advantages of air PC cooling is its simplicity. There are no moving parts other than the fan, making it reliable and easy to maintain. Additionally, modern air coolers are designed to be highly efficient, with some high-end models rivalling the performance of liquid cooling systems. However, air cooling can be limited by the size of the heatsink and the airflow within the PC case, which is why proper case ventilation is crucial.
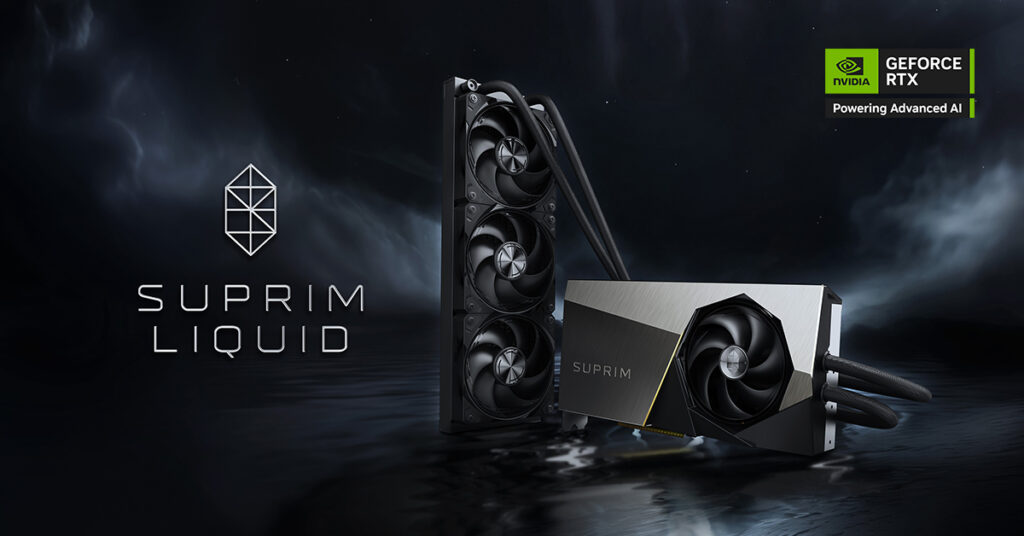
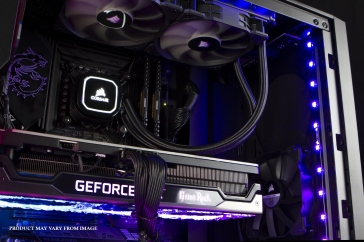
Liquid cooling: Advanced heat dissipation
Liquid cooling, also known as water cooling, is a more advanced solution that offers superior heat dissipation compared to air cooling. In a liquid PC cooling system, a coolant (usually a mixture of water and antifreeze) circulates through a loop that includes a water block, pump, radiator, and tubing. The water block is attached to the central processing unit (CPU) or graphics processing unit (GPU), where it absorbs heat. The heated coolant is pumped to the radiator and cooled by fans before being recirculated.
Liquid cooling can handle higher thermal loads, making it ideal for overclocked systems or high-performance gaming PCs. It also tends to be quieter than air cooling, as the radiator fans can run at lower speeds. However, this system is costlier and more complex, requiring regular maintenance to prevent issues like coolant leaks or pump failures.

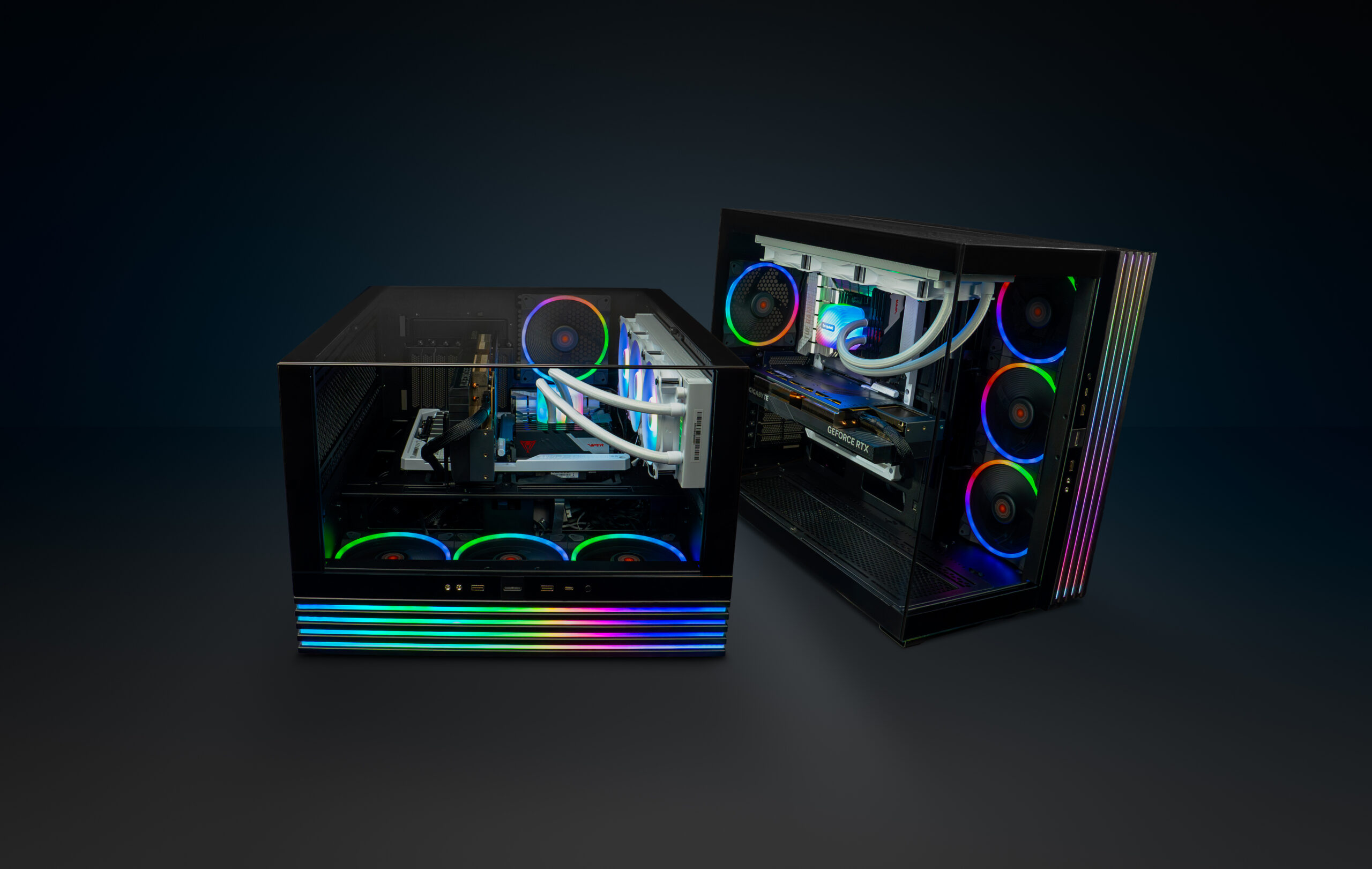
The role of case design and airflow
No matter how advanced your PC cooling system is, its effectiveness depends largely on the design of your PC case and the airflow within it. A well-ventilated case with strategically placed fans can significantly improve cooling performance by ensuring a steady supply of cool air and efficient expulsion of hot air. Many modern cases feature mesh panels, dust filters, and customisable fan mounts to optimise airflow and reduce dust buildup.
Cable management maintains good airflow. Cluttered cables can obstruct the path of air, leading to hotspots and reduced cooling efficiency. By organising cables and using modular power supplies, you can create a cleaner interior that promotes better airflow and cooling.
Bottom line
Gaming PC cooling systems are a vital component of any high-performance rig, ensuring that your hardware stays cool and operates at peak efficiency. By investing in a robust cooling setup and paying attention to case design and airflow, you can enjoy smoother gameplay, longer hardware life, and the satisfaction of knowing your PC is running at its best.


For even more helpful guides like this, click right here.